Precision Oncology
What is "methylation"?
How can we precisely explore the changes within the body?
What is DNA methylation?
DNA methylation is a major epigenetic modification, and changes in the methylation pattern play a crucial role in the development of tumors. Since DNA methylation occurs almost throughout the entire process of tumor development, including precancerous lesions, it may be an ideal biomarker for early cancer diagnosis. In many types of lung cancer samples, various abnormal promoter methylation of genes have been evaluated as biomarkers.[1]
A single blood sample reveals traces of the tumor
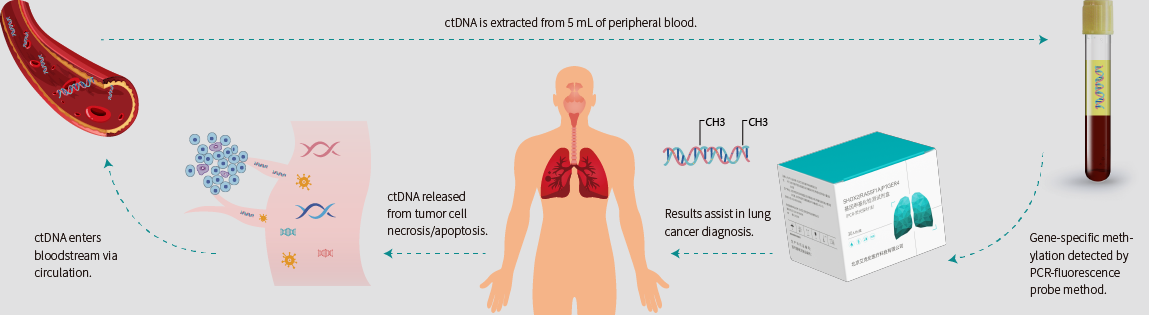
After the tumor cells carrying genetic information and epigenetic alterations undergo necrosis or apoptosis, they release fragmented genomic DNA into the peripheral blood, which is known as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).[2]By capturing these trace amounts of ctDNA and detecting the specific changes in tumor methylation sites, this method can provide earlier and more accurate information on the occurrence and development of tumors compared to traditional detection techniques.[3]
Reference:
[1] Rajabi H , Tagde A , Alam M , et al. DNA methylation by DNMT1 and DNMT3b methyltransferases is driven by the MUC1-C oncoprotein in human carcinoma cells[J]. Oncogene, 2016.
[2]Wan, J.C.M. et al. (2017) Liquid biopsies come of age: to-wards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat.Rev. Cancer 17, 223–238
[3]Gao Y, et al. Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing analysis of circulating tumour DNA for the detection and molecular classification of cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2022 Aug;12(8):e1014.